If you follow my articles, and used to follow my previous blog site (smartsupplychains.ai), I first wrote about leveraging LLMs for customized Enterprise applications back in 2019. That was the pre ChatGPT era.
My postulation was that variations of LLMs can be used to build models that understand an organization’s custom data. My take on this was that within 3-5 years, we will see such technologies emerge in production. The good news is that since I could think of an application like this, people much smarter than me were already thinking about it. The concept of RAGs came into existence in 2020! And that led to the prediction coming true.
Patrick Lewis, in his 2020 paper, Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks, postulated the RAG architecture, which has since then take-off widely. RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation and addresses a key shortcoming of LLMs.
The leading LLM models we are familiar with have one drawback. I assume you are familiar with LLMs, essentially neural networks with a mind-boggling number of parameters. These parameters capture how we use language, precisely words, to formulate sentences. However, post-training, it may struggle if you want the model to respond to more recent or current context data.
Remember the hallucination incidences where lawyers submitted references generated by GPTs, which were eventually found to be totally made up? RAGs can address that as well. Let us understand in simple English, what RAGs essentially help with.
Retrieval-augmented generation provides a link between generative AI services and external resources, specifically sources that are rich in the latest technical details. RAGs can be used by LLMs to connect with external data sources. This means that if users have access to a LLM model, they can use that to interface with their internal data repositories. Figure 1, from the research paper cited above, provides a good representation of how RAGs work with LLMs. You can ignore the technical aspects and just pay attention to the two key aspects illustrated:
Figure 1: Overview of RAG approach
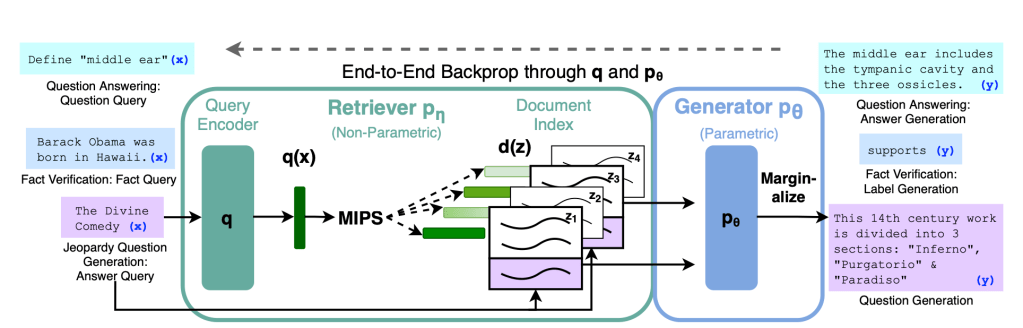
Source: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks
- Retriever works in tandem with the generator
- Retriever helps provide the generator more context-rich and accurate data
So, you can simplify Figure 1 above into Figure 2, which shows retriever can tap into external and internal repositories and aid the LLM.
Figure 2: Simplified architecture of RAGs
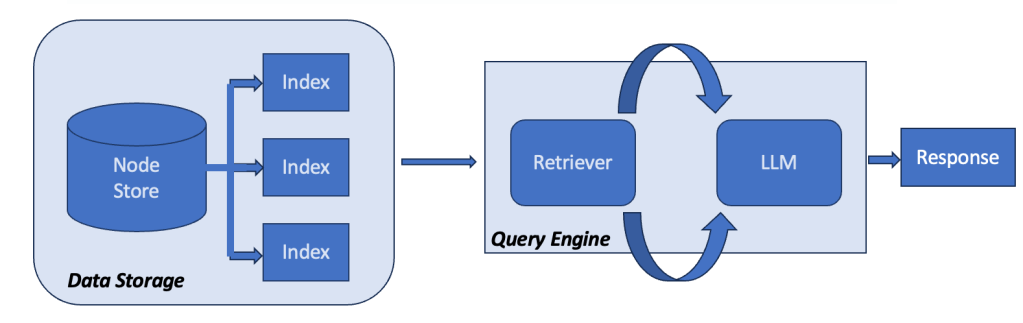
This makes RAG an excellent tool for infusing the power of LLMs into enterprise analytics. Supplementing LLMs with RAG can enhance existing data-rich enterprise tools. That is why leading ERP and enterprise software companies have embraced this model to provide tools that can fundamentally change how business processes and planning run within organizations. Once companies understand how to leverage RAG, they can leverage a plethora of off-the-shelf or customized LLMs with internal or external knowledge repositories. This will allow them to build various assistant bots to help their employees and customers. Many organizations have already taken this path. The secret sauce is to make these assistants more and more productive by enhancing the context and training.
To summarize, RAGs can help improve LLM performance in multiple ways, like:
- Enriching context
- Enhancing diversity of the text
- Ensuring information is up to date
- Improving consistency
- Allowing companies to leverage their enterprise data with LLM models
In a separate article, we will review some use cases of how RAG-powered assistants can help users get insights that essentially democratize analytics in enterprises.

