This article is a part of a series of articles on Swarm intelligence. Please refer the appendix section for links to previous articles in this series.
Elephant Herd Optimization (EHO)
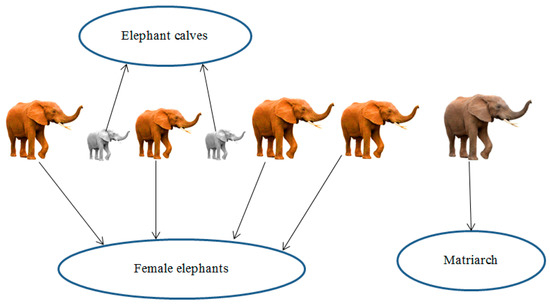
Elephants are social creatures that live in herds and follow a social structure. They live primarily in social structures of female elephants and calves headed by a matriarch. The herd is firmly bonded, and the protection of calves is considered the responsibility of the entire herd. While females tend to follow the herding behavior, males prefer not to be part of these herds. Male elephants, as they become adults, gradually become independent of their herds and eventually leave them entirely. Although male elephants live away from their herds, they can stay in contact with elephants in their herd through low-frequency vibrations. This herding behavior of elephants, shown in Figure 1, has been captured in Elephant herd optimization algorithms.
Figure 1: Elephant Herding Behavior
Source: Elephant Herding Optimization: Variants, Hybrids, and Applications
The EHO technique was proposed by Wang et al. in 2015. As mentioned previously, the algorithm was developed after studying natural elephant herding behavior. The following assumptions are incorporated into EHO Algorithm..
(1) The elephant population comprises clans with a fixed number of elephants in each clan.
(2) A fixed number of male elephants will leave their clans and live away from the main group in each generation.
(3) Each clan is led by a matriarch elephant.
In EHO, we use these herding rules to simplify the problem. After separating the worst values from the population, the fittest values are updated using the clan updating operator, and the worst values are discarded.
- It is assumed that the total population of elephants is divided into two groups such as clans. These clans have a definite number of elephants.
- It is also assumed that the worst-performing male elephant will leave their family group. It lives alone at a distance from the elephant group.
- The matriarch is the leader of all elephants who live in a clan.
Applications
EHO finds applications in many categories of optimization problems like:
- Continuous optimization
- Constrained optimization
- Multi-objective optimization
Of these three, I believe the algorithm is a good fit for continuous optimization scenarios in supply chain. Let us explore some examples I found in my readings.
Continuous optimization
Within continuous optimization, two key areas seem to be of interest. Those areas are:
- Scheduling
- Image processing
You can find links to research papers in the two categories below.
Scheduling
The algorithm seems to be an efficient fit for scheduling problems. Most research papers I found were focused on scheduling in power grid systems, like the first three examples in the list below. But these can be easily extrapolated into supply chain scheduling.
- Stochastic operational management of grid-connected microgrid under uncertainty of renewable resources and load demand
- Optimal Virtual Power Plant Scheduling Using Elephant Herding Optimization
- Scheduling of appliances in home energy management system using elephant herding optimization and enhanced differential evolution
- Mathematical models and an elephant herding optimization for multiprocessor-task flexible flow shop scheduling problems in the manufacturing resource planning
Of particular interest to you should be the last one on the list above. It can be leveraged in complex job scheduling scenarios in smart manufacturing, coupled with deep learning, to make it practical for real-time application scenarios. The other scheduling applications must also be coupled with deep learning if they are to be leveraged for tactical planning.
Image Processing
Another exciting area that can be extrapolated in the supply chain world to build innovative image recognition-powered applications is using this algorithm in image recognition. Some examples of research papers have been highlighted below.
- Multi-level Image Thresholding Using Elephant Herding Optimization Algorithm
- Nature inspired optimization techniques for image processing
- .Land-use/land-cover classification using elephant herding algorithm
Note the last one on this list. Remember the article I wrote on mitigating the housing crisis by reclassifying land use and zoning using AI (Can Analytics Help Address The Housing Scarcity?)? This is an example of how AI can be leveraged in such scenarios.
We will continue our journey of swarm intelligence algorithms in the subsequent article. The article will be published on 12/8.
Appendix
This article is part of a series of articles. Previous parts of this article series can be found here:

