This article is part of a series of articles. Previous parts of this article series can be found here:
Chicken Swarm Optimization(CSO)
Chicken Swarm Algorithms (CSOs) capture three key behaviors of a chicken swarm population:
- Multiple groups exist within a population
- Each group has a hierarchy and relationships exist within the group population
- Groups are territorial when foraging for food
Any large chicken population consists of multiple groups within their distinct territories. Within each group, there is a hierarchal order. As in most species in the animal kingdom, dominant chickens in the group will dominate the weak. In their social structure, there is a head rooster, as shown in Figure 1. There also exists a dominant group of hens that remain near the roosters. Then there are submissive hens who stand at the fringes (periphery) of the group.
Figure 1: Overview of chicken swarm behavior in CSO.
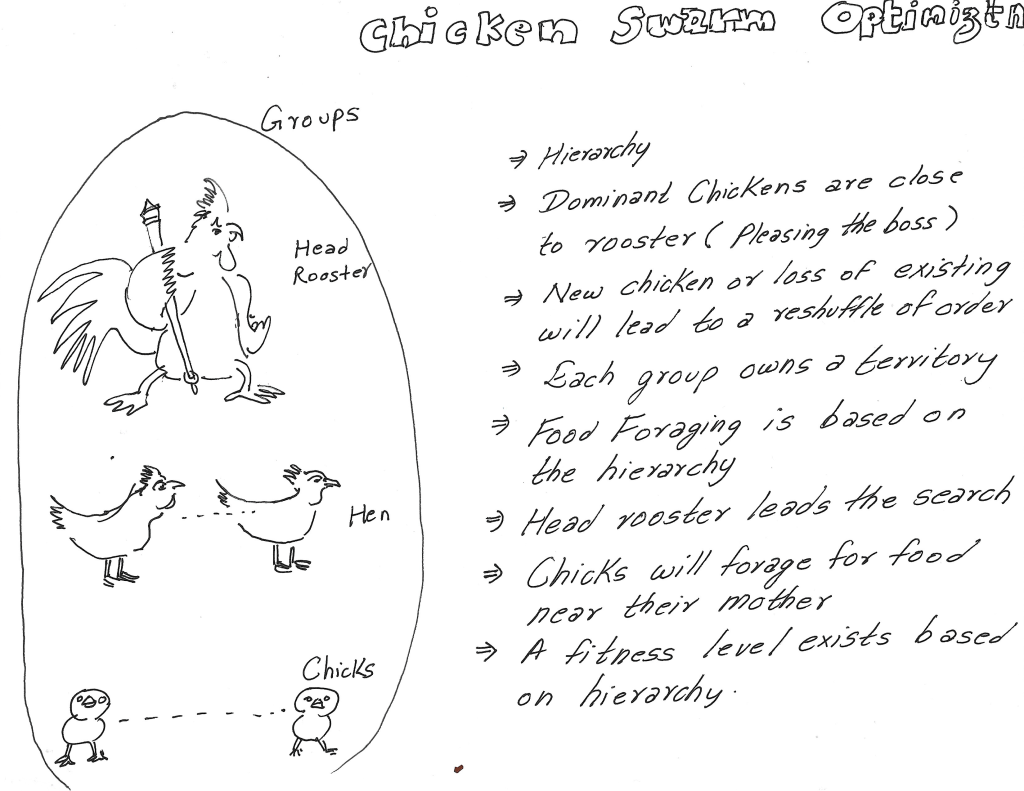
A change in population disturbs the hierarchy and the group essentially readjusts the hierarchy. A sudden increment or decrement in the number of chickens from a group would cause temporary chaos to their social structure. However, until the hierarchial order is eventually established again.
The behavior of chickens also varies with gender. The head rooster takes the lead when foraging for food and is also responsible for safeguarding the territory by fighting with chickens who invaded the territory the group inhabits. The head rooster is assisted by dominant chickens to forage for food. The submissive chickens remain at the group’s periphery to search for food. The food foraging behavior, constrained by hierarchy, has been shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Chicken swarm foraging behavior
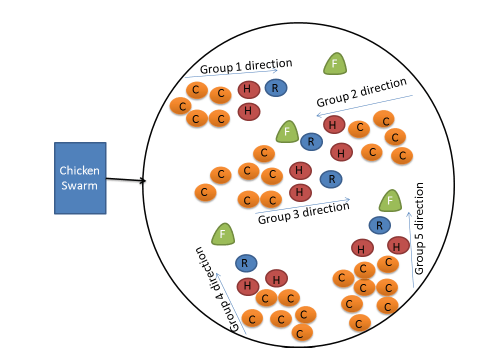
Source: ResearchGate
Broad steps of leveraging the algorithm-an example
Let us review the high-level broad steps of CSO algorithm.
- We start with defining a population of chickens; no. of roosters, hens, chicks;
- You define the number of iterations of movements
- Since fitness is at the core of this algorithm, we categorize chicken groups into rooster, hen and chick, based on fitness values
- For each group, we define the relationships within the group (Like mother-chick and rooster-hen)
- We define the movement of the rooster to maximize the fitness level.
Applications of CSO
The algorithm has a wide gamut of applications, at least in the theoretical arena. Since at the core of this algorithm lies to concept of motion with best fitness value, it is a good fit to find solutions to Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). Which makes it obviously a good candidate for VRP problems. This paper, Solving Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem Using Chicken Swarm Optimization with Genetic Algorithm, covers this specific application.
If we keep functional business applications aside, chicken swarm algorithms can also help us in machine learning engineering. One example is feature selection. And this is not theoretical. I consulted numerous research papers., Based on those papers, like A novel chaotic chicken swarm optimization algorithm for feature selection, CSO is widely leveraged for feature selection, and variations of it are consistently being tried to enhance capabilities.
The classification capabilities of CSO make them a good candidate for problems where classification is the core of the solution. Among many other papers, I also found our favorite churn detection one. This paper, Leveraging Metaheuristics with Artificial Intelligence for Customer Churn Prediction in telecom industries, highlights CSO’s role in an AI algorithm for churn detection.I loved this paper because it highlights the powerful combination of AI and optimization. The high-level components of this solution has been illustrated in Figure 3.
Returning to the supply chain world, I think one of the most prominent applications, other than the VRP example above, is asset management in the Industry 4.0 context. The algorithm is a good fit for fault detection in Industrial equipment, as highlighted by the following papers.
- Chicken Swarm Optimization with Deep Learning Based Packaged Rooftop Units Fault Diagnosis Model
- Effective Rotor Fault Diagnosis Model Using Multilayer Signal Analysis and Hybrid Genetic Binary Chicken Swarm Optimization
- Fault detection involving unfavorable interaction effects to enhance the fault diagnostics of refrigeration systems in commercial supermarkets
In the next part of this series, we will explore cockroach swarm optimization. The article will be published on 12/5.